|
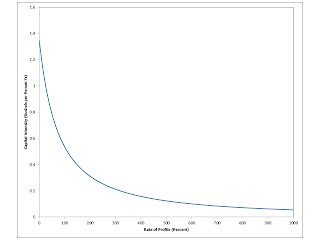
| Figure 1: Wage-Rate of Profits Curves and their Frontier |
1.0 Introduction
This post is a generalization of a neoclassical one-good model. It advances a comparison of Sraffian analysis of the choice of the cost-minimizing choice of the technique and neoclassical analyses, correctly understood, of marginal productivity. Accordingly, all production functions are smooth in this example. If substitutability is seen as a technological property of production functions, then the single capital good and labor can be substituted in each of the two industries in this model.
2.0 The Technology
Consider a simple economy in which steel and corn are produced from inputs of steel and labor. The steel used as an input in production is totally used up in yearly cycles, and the outputs become available at the end of the year. In other words, this is a model without fixed capital, and all production processes require a year to complete.
2.1 Production Functions
The production function for steel is:
Q1 = F1(X1, L1) = A1 X1α1 L1(1 - α1)
where:
- Q1 is (gross) output of steel (in tons).
- X1 is steel (tons) used as a capital good in the steel industry.
- L1 is labor (person-years) used as an input in the steel industry.
and A1 and α1 are positive constants such that:
0 < α1 < 1
The production function for corn is:
Q2 = F2(X2, L2) = A2 X2α2 L2(1 - α2)
where:
- Q2 is (gross) output of corn (in bushels).
- X2 is steel (tons) used as a capital good in the corn industry.
- L2 is labor (person-years) used as an input in the corn industry.
and A2 and α2 are positive constants such that:
0 < α2 < 1
2.2 A Set of Coefficients of Production
An alternative specification of this Constant-Returns-to-Scale (CRS) technology is as a set of coefficients of production a01(s1), a02(s2), a11(s1), a12(s2) from the set:
{ (a01(s1), a02(s2), a11(s1), a12(s2)) | 0 < s1, 0 < s2}
where:
a01(s1) = [1/(A1s1)][1/(1 - α1)]
a02(s2) = [1/(A2s2)][1/(1 - α2)]
a11(s1) = s1(1/α1)
a12(s2) = s2(1/α2)
and
- a01(s1) is the labor required, in the steel industry, per ton steel produced.
- a02(s2) is the labor required, in the corn industry, per bushel corn produced produced.
- a11(s1) is the steel input required, in the steel industry. per ton steel produced (gross).
- a12(s2) is the steel input required, in the corn industry, per bushel corn produced.
2.0 Quantity and Price Equations, Given the Technique
Consider a stationary state in which the firms employ one person-year of labor each year, and prices are stationary. For notational convenience below, define the following function:
f(R) = (a01a12 - a02a11)R + a02
2.1 Quantity Relations
The amount of steel produced each year, measured in tons, is:
q1 = a12/f(1)
The amount of corn produced each year, measured in bushels, is:
q2 = (1 - a11)/f(1)
These quantities must satisfy two equalities. First, the amount of labor employed is unity:
1 = a01q1 + a02q2
Second, consider the following equation:
q1 = a11q1 + a12q2
The left-hand side of the above equation denotes the quantity of steel produced each year and available, as output from the steel industry, at the end of each year. The right-hand side denotes the sum of steel used as inputs in the steel and corn industries, respectively. These inputs must be available at the start of each year. Hence, the above equation is a necessary condition when the economy is in a self-sustaining, stationary state.
2.2 Price Relations
I take the consumption good, corn, as the numeraire. The price of steel, in units of bushels per ton, is
p = a01/f(1 + r),
where r is the rate of profits. The wage is:
w = [1 - a11(1 + r)]/f(1 + r)
The above equation is known as the wage-rate of profits curve.
The price of steel, the wage, and the rate of profits must satisfy two equations. The condition that the price of steel just cover the cost of producing steel is:
pa11(1 + r) + a01w = p
The left-hand side of the above equation shows the cost of producing a ton of steel. Costs are inclusive of normal profits, so to speak, on the cost advanced to purchase physical inputs at the start of the year. In this case, those inputs consist of steel, the single capital good in this model. Although labor is hired at the start of the year to work throughout the year, the price equations in this model show labor being paid out of the harvest gathered at the end of the year.
The condition that the price of corn just cover the cost of producing corn yields a similar equation:
pa12(1 + r) + a02w = 1
2.3 The Capital-Labor Ratio
"Capital" is an ambiguous term. It denotes both physically-existing means of production. And it denotes the value of those means of production, when embedded in certain social relations. For example, in this model, the distribution of the capital goods over the two industries is assumed to be appropriate to the continued self-reproduction of the economy. In a sense, the plans of entrepreneurs and firms managers are coordinated.
At any rate, the relationships described so far allow one to express the value of capital, in numeraire units, per person-years, given the technique:
k = p q1
k = a01a12/[f(1)f(1 + r)]
The capital-labor ratio (in units of bushels per person-years) does not appear in any legitimate marginal product. Nevertheless, I find it a useful quantity for further analysis in multicommodity models.
3.0 The Chosen Technique
The cost-minimizing technique differs with the rate of profits. For analytical convenience, I take the rate of profits as exogenous in this model. One could, instead, if one so chose, take the wage as given and find the rate of profits endogenously. At any rate, this model is open, and the distribution of income is not determined in the model. The equations below set out each of the four coefficients of production in this model as functions of the rate of profits:
a01 = (1/A1)[1/(1 - α1)] [(1 + r)/α1][α1/(1 - α1)]
a02 = (1/A2)
x {(1 - α2)/[(α1)[α1/(1 - α1)](1 - α1)α2]}α2
x [(1 + r)/A1][α2/(1 - α1)]
a11 = α1/(1 + r)
a12 = (1/A2)
x [(α1)[α1/(1 - α1)](1 - α1)α2/(1 - α2)](1 - α2)
x [A1/(1 + r)](1 - α2)/(1 - α1)
3.1 Steel as a Basic Commodity and the One-Good Case
I have previously set out an analysis of the choice of technique for a one-good model with an aggregate Cobb-Douglas production function. In the two-good model set out in this post, the coefficients of production for steel, a01 and a11, when the cost-minimizing technique is chosen, are the same as the coefficients of production in that one-good model. This is not surprising.
In the model in this post, steel enters, as an input, into the production of both steel and corn, for all possible techniques. On the other hand, corn never enters as an input into the production of any commodity. In the technical terminology of post-Sraffian economics, steel is always a basic commodity, and corn is never a basic commodity. Thus, the production of steel can be analyzed, in some sense, prior to the analysis of the production of corn.
3.2 A One-Good Special Case
Consider the special case in which:
α1 = α2 = α
A1 = A2 = A
In effect, steel and corn are the same commodity. The coefficients of production, for the cost-minimizing technique are:
a02 = a01 = (1/A)[1/(1 - α)] [(1 + r)/α][α/(1 - α)]
a12 = a11 = α/(1 + r)
So this case reduces to the one-good model, as it should. This concludes my analysis of this special case.
4.0 The Chosen Technique on Unit Isoquants and Marginal Productivity Conditions
The coefficients of production are such that the steel industry lies on its unit isoquant:
1 = F1(a11, a01)
Likewise, the corn industry lies on its unit isoquant:
1 = F2(a12, a02)
Since the coefficients of production in Section 3 above are for the cost-minimizing technique, all valid marginal productivity relationships must hold. I have chosen to express each marginal productivity condition in numeraire units per unit input. And, the cost of an input and its marginal product are equated here at the end of the year.
Following these conventions, the following display equates the cost of steel to the value of the marginal product of steel in the steel industry:
p(1 + r) = p ∂F1(a11, a01)/∂a11
Likewise, the following display equates the cost of steel to the value of the marginal product of steel in the corn industry:
p(1 + r) = ∂F2(a12, a02)/∂a12
Since wages are paid out of the harvest, the rate of profits does not appear in my statement of marginal productivity conditions for labor. The following display equates the wage and the value of the marginal product of labor in the steel industry:
w = p ∂F1(a11, a01)/∂a01
Likewise, the following display equates the wage and the value of the marginal product of labor in the corn industry:
w = ∂F2(a12, a02)/∂a02
I have checked the above equations for the isoquants and the four marginal productivity equations. This is quite tedious.
Above, I have listed six equations, two expressing the condition that the coefficients of production lie upon unit isoquants and four marginal productivity equations. These six equations are sufficient to determine the six unknowns (w, p, a01, a02, a11, and a12) in terms of the model parameters and the externally specified rate of profits. In other words, this model illustrates that marginal productivity is a theory of the choice of technique, not of the (functional) distribution of income.
5.0 The Wage-Rate of Profits Frontier
An alternate analysis of the choice of technique can be based on the wage-rate of profits frontier. And this analysis yields the same answer as the above analysis based on marginal productivity.
Recall, from Section 2.2, that a technique can be specified as an ordered pair chosen from the specified index set. The index variables for the cost-minimizing technique, as a function of the rate of profits are:
s1 = [α1/(1 + r)]α1
s2 = (1/A2)α2
x [(α1)[α1/(1 - α1)](1 - α1)α2/(1 - α2)][(1 - α2)α2]
x [A1/(1 + r)][(1 - α2)α2/(1 - α1)]
I think it of interest to note that both the optimal process for producing steel and the optimal process for producing corn, in a stationary state, vary continuously with the rate of profits. This is not a generic result for a discrete technology. In a discrete technology, the cost-minimizing techniques at a switch point typically differ in the process used in only one industry; a small variation in the rate of profits thus affects only the specification of a process in one industry.
5.1 First Order Conditions
Since the coefficients of production are functions of the index variables, the wage-rate of profits curve for a technique can be viewed as a function of:
- The index variables s1 and s2,
- The rate of profits r, and
- The model parameters α1, A1, α2, and A2.
A necessary condition for a technique to be cost-minimizing, at a given rate of profits, is that the wage be a maximum. This maximum is taken from the wage on each wage-rate of profits curve, over all techniques. In the current context, with a model with smooth production functions, the first derivative of the wage-rate of profits frontier, with respect to each index variable, must be zero at the maximum:
∂w/∂s1 = 0
∂w/∂s2 = 0
Note that the above is a system of two equations in the two unknown index variables. I did not actually calculate the above derivatives for this model. Perhaps Figure 1 provides some confidence in this mathematics. I deliberate drew three wage-rates of profits curves on the frontier and one off of it.
5.2 Second Order Conditions
The FOCs determine a critical point. The calculus is consistent with such a critical point being a local maximum, a local minimum, or a saddle point. The following are sufficient conditions, in this context, for a critical point to be a local maximum:
∂2w/∂s12 < 0
∂2w/∂s22 < 0
D(s1, s1) > 0
where D(s1, s1) is defined by:
D(s1, s1) = [∂2w/∂s12][∂2w/∂s22] - [∂2w/∂s1∂s2]2
Of the three SOCs, either the first or the second is redundant.
6.0 Conclusion
I still have some ideas for future work with this model. But I think this is enough for one blog post. I hope the above presentation suggests that marginal productivity is not a theory of distribution, in general. One cannot validly hold, for example, that real wages are determined by the marginal product of labor. Furthermore, the Sraffian analysis of the choice of technique is analytically equivalent to the determination of the choice of technique, given, for example, the rate of profits, by marginal productivity.